Solar panels for homes harness sunlight via photovoltaic cells, converting it to electricity. This environmentally sustainable technology reduces carbon footprints and annual energy bills by 30-40%. Governments offer incentives and rebates for installation, offsetting upfront costs. Efficient panels, proper installation, and safety protocols ensure optimal performance and savings. Solar power reduces grid dependency, leading to long-term financial benefits and environmental stewardship.
In today’s world, the transition to sustainable energy sources is not just a trend but an imperative for both environmental stewardship and economic viability. Solar panels for homes have emerged as a powerful tool in this endeavor, offering homeowners a way to generate clean, renewable electricity while reducing their carbon footprint. However, navigating the complexities of solar technology can be daunting for many. This article provides a comprehensive, authoritative breakdown of solar panels for homes, demystifying the process and empowering readers to make informed decisions about adopting this game-changing technology.
Understanding Solar Panels for Homes: A Basic Guide
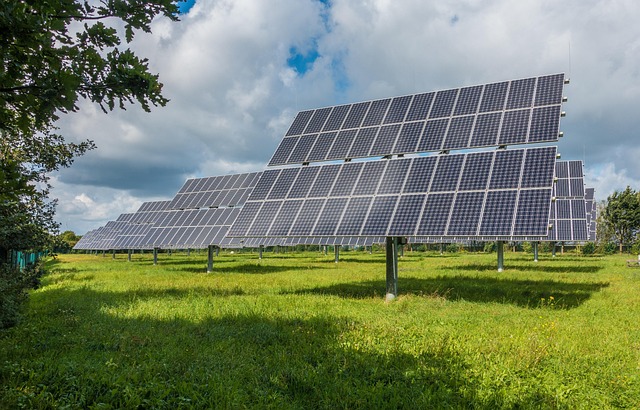

Solar panels for homes have emerged as a popular and increasingly accessible solution for harnessing renewable energy. To understand their potential fully, homeowners must grasp the basics of how these systems work and what they offer. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, catering to those new to the concept, aiming to demystify solar panel technology and its benefits.
At their core, solar panels for homes are designed to convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells are composed of semiconducting materials that generate a direct current (DC) when exposed to sunlight. In simpler terms, as photons from the sun strike the cells, they excite electrons, creating a flow of electric charge. This DC power is then funneled through wires to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC), suitable for use in homes. AC electricity powers most home appliances and is what utilities companies measure for billing purposes.
One of the key advantages of solar panels for homes is their environmental sustainability. By harnessing the sun’s energy, homeowners can significantly reduce their carbon footprint, contributing to global efforts against climate change. For borrowers considering solar panel installations, understanding the financial implications is crucial. While upfront costs can be substantial, many governments offer incentives and rebates to offset these expenses, making it a more viable option. According to recent data, the average residential solar panel system in [location] reduces electricity bills by 30-40% annually for borrowers who finance their installations through loans with competitive interest rates. As the technology advances, so does its affordability, attracting more homeowners and driving down borrower requirements.
How to Install Solar Panels on Your Home: Step-by-Step
Installing solar panels on your home is a significant step towards embracing renewable energy sources and reducing your carbon footprint. This process involves careful planning, technical expertise, and adherence to safety standards. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how to install solar panels for homes, guiding you through each crucial stage.
First, assess your home’s suitability for solar power by evaluating its roof structure, shading potential from surrounding trees or buildings, and the overall size of the available space. Ensure that your roof can support the weight of the panels and that there’s adequate sunlight exposure throughout the year. Next, research local regulations and permits required for solar panel installation. Many areas have specific codes and guidelines to ensure safety and compliance, so it’s essential to understand these borrower requirements before proceeding.
Once approved, select a reputable solar panel provider and installer. Consider factors like their experience, warranties offered, and the types of panels they provide. High-efficiency panels are increasingly popular due to their superior energy production capabilities. After contracting with an installer, they will conduct a thorough site inspection, design a custom system tailored to your needs, and provide a detailed quote outlining costs and expected energy savings. This is also when you’ll learn about available incentives or rebates from local, state, or federal programs to offset the initial installation costs.
On the day of installation, the team will safely mount the solar panels on your roof, connect them to an inverter that converts DC power into AC power suitable for your home’s electrical system, and then wire everything to your breaker box. Throughout this process, safety protocols are paramount. After completion, test the system thoroughly, ensuring all components function as intended. Finally, monitor your energy production and savings over time, allowing you to track the environmental benefits of your solar panel installation.
Benefits and Cost Savings of Solar Power for Homes

Solar panels for homes have emerged as a powerful tool for homeowners looking to reduce energy costs and their carbon footprint. The benefits of adopting solar power extend far beyond environmental advantages, offering significant cost savings and increased financial stability for property owners. By harnessing the sun’s energy, households can achieve energy independence and take control of their utility expenses.
One of the most tangible benefits is the reduction in electricity bills. Solar panels for homes generate clean, renewable energy from sunlight, which can offset a substantial portion of a household’s power requirements. According to recent studies, homeowners with solar installations can save an average of 20-30% on their annual energy costs. For example, a typical U.S. home using 10,000 kWh annually could potentially save around $1,500-$2,000 per year by leveraging the power of the sun. This savings can be even more substantial in regions with higher electricity rates or larger homes. Moreover, many governments and local utilities offer incentives and rebates for solar panel installations, further enhancing the financial benefits for borrowers who invest in this clean energy technology. The borrower requirements for these programs vary but often include specific criteria related to system size, energy production, and local regulations, ensuring a well-structured and beneficial implementation of solar panels for homes.
Over time, solar power can lead to substantial long-term savings, as it eliminates the need for continuous purchases of conventional energy from the grid. This shift not only reduces expenses but also contributes to a more sustainable future. Additionally, with advancements in technology, solar panels are becoming increasingly efficient, allowing homeowners to generate more electricity while requiring less space on their rooftops. This efficiency gains are particularly beneficial for those living in urban areas or smaller homes, making solar power accessible and attractive to a broader range of borrowers.
