Solar panels for homes harness photovoltaic technology to convert sunlight into electricity, offering energy independence, cost savings, and sustainability. Investors must consider property assessment, financing options (including tax credits), and installation processes involving detailed assessments, equipment selection, and skilled technician deployment. The global trend indicates solar panels as a lucrative investment, with 2021 capacity reaching 800 gigawatts and projections to meet 40% of global electricity demands by 2050. Investing in solar panels for homes yields long-term gains and environmental benefits.
In the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, solar panels for homes have emerged as a prominent and lucrative investment opportunity. As the world transitions towards cleaner power sources, understanding the potential of residential solar installations is paramount for investors seeking long-term profitability and environmental impact. This article provides an in-depth exploration of solar panel systems specifically tailored for homes, delving into their functionality, economic benefits, and the compelling case for investors to embrace this renewable energy revolution. By the end, readers will grasp the transformative power of solar panels for homes and their pivotal role in shaping a sustainable future.
Understanding Solar Panels for Homes: Basics and Benefits
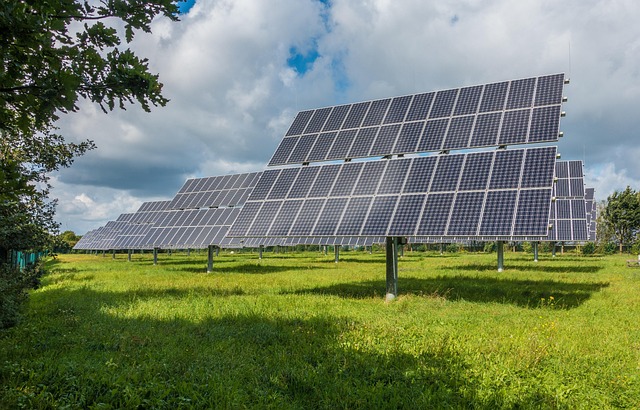

Solar panels for homes have emerged as a transformative technology, offering both environmental benefits and financial advantages to homeowners. At its core, solar power leverages the energy from sunlight to generate electricity, providing a clean and renewable alternative to conventional energy sources. When installed on residential properties, solar panels can significantly reduce utility bills and contribute to a smaller carbon footprint.
The basics of solar panel functionality involve capturing photons from sunlight using photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity, which is then inverted to alternating current (AC) for use in homes. The benefits of adopting solar panels for homes are multifaceted. Firstly, it offers long-term cost savings with a potential reduction in electricity bills over time. Homeowners can also take advantage of various incentives and rebates offered by governments and utilities to offset the initial installation costs. Moreover, solar energy is highly reliable, as once installed, it provides free electricity without dependence on utility rates that can fluctuate.
For investors considering solar panels for homes, understanding borrower requirements is essential. Lenders typically assess the financial viability of solar installations through methods like loan-to-value (LTV) ratios and debt service coverage ratios. Typically, these loans are structured as a percentage of the home’s value, with optimal LTV ranges varying between 80% to 90%. However, with the growing popularity of solar energy, some lenders are introducing specialized solar loans designed specifically for homeowners looking to install solar panels. Such financing options can streamline the process and make solar power more accessible, allowing investors to capitalize on the expanding market for renewable energy solutions in residential settings.
How Solar Panel Systems Work in Residential Settings

Solar panels for homes have emerged as a powerful tool for residential energy independence and sustainability. At their core, solar panel systems harness the sun’s radiant energy, converting it into usable electricity through photovoltaic (PV) technology. This clean and renewable process offers significant advantages for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint and lower energy costs.
In a residential setting, solar panels are typically installed on rooftops or open spaces where they receive unobstructed access to sunlight. These panels consist of many individual PV cells that absorb sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity. Inverters then convert this DC power into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form used in most homes. The generated electricity can either be used immediately, providing power for lights, appliances, and heating/cooling systems, or stored in batteries for later use.
For investors considering solar panels for homes, understanding the borrower requirements is essential. Banks and lending institutions often assess a property’s potential for solar energy generation as part of their loan evaluation process. Factors such as location, roof structure, sunlight exposure, and local incentives play a significant role in determining the feasibility and financial viability of solar panel installations. According to recent data, residential solar adoption has been steadily growing, with many states offering tax credits and rebates to encourage the transition to clean energy. This trend highlights the changing landscape of energy consumption and the increasing appeal of solar panels for homes as a sustainable investment option.
Financial Considerations: Investing in Solar for Your Home
Investing in solar panels for homes can be a lucrative venture for savvy investors looking to diversify their portfolios with sustainable energy assets. The financial considerations involved in adopting solar power for residential properties are complex yet rewarding. Understanding these aspects is crucial for any investor contemplating this green initiative.
One of the primary attractions is the potential for significant cost savings over time. Solar panels for homes reduce electricity bills, as they harness the power of the sun, a free and renewable resource. Many homeowners and investors alike have benefited from lower energy expenses, especially in regions with high utility rates. According to recent studies, residential solar installations can save an average of 20-30% on energy costs annually. These savings can be substantial over the long term, making solar a sound investment strategy.
Borrower requirements for solar panel installations have evolved to make financing more accessible and attractive. Many lenders now offer specialized solar loans with competitive interest rates, allowing homeowners to pay for their systems over time through monthly installments. This approach makes it possible for investors to recover their initial investments within a reasonable timeframe while enjoying the benefits of clean energy production. For example, a typical residential solar panel system in the United States can cost between $15,000 and $25,000, with loan terms ranging from 10 to 25 years. Careful consideration of these borrower requirements is essential for investors aiming to maximize their returns on solar-powered homes.
Additionally, government incentives and tax credits play a significant role in making solar energy more accessible and profitable. Many countries offer tax breaks, grants, or rebates to encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources. For instance, the U.S. federal income tax credit for residential solar systems has been instrumental in driving investment in solar panels for homes. Investors should research these incentives, as they can significantly impact the overall financial viability of a solar project. By combining cost savings, attractive financing options, and favorable government policies, investors can make informed decisions regarding their investments in solar-powered properties, ensuring long-term profitability and contributing to a sustainable future.
Installation Process: From Planning to Completion

The installation process of solar panels for homes involves a series of meticulous steps, from initial planning to final completion. It begins with a thorough assessment of the property’s energy needs and roof structure, ensuring compatibility and maximizing sunlight exposure. Solar panel experts conduct on-site inspections, taking measurements and evaluating shading potential from surrounding structures or trees, which is crucial in determining the efficiency of solar panels for homes. This initial phase sets the foundation for the entire project.
Upon approval, the selection of equipment starts, tailored to the borrower’s requirements. Solar panels for homes are available in various sizes and technologies, each with unique benefits. Borrowers may opt for a full-scale installation, utilizing premium panels, or choose a more budget-friendly approach, balancing quality and cost. The next step involves obtaining necessary permits from local authorities, ensuring compliance with regulations. This process can vary regionally, necessitating knowledge of local guidelines to streamline the solar panels for homes borrower requirements efficiently.
Installation proper entails precise positioning of panels, wiring, and connection to the property’s electrical system. Skilled technicians ensure optimal orientation and angle for maximum sunlight capture throughout the year. During completion checks, performance testing is conducted to verify the system’s efficiency, addressing any potential issues before final handover. This meticulous approach guarantees not only optimal energy generation but also peace of mind for homeowners investing in solar panels for homes.
Long-Term Gains: The Future of Solar Energy for Homes

Solar panels for homes have emerged as a lucrative investment opportunity, offering significant long-term gains in the rapidly evolving energy sector. The future of solar energy is bright, driven by decreasing costs and increasing efficiency of solar panels for homes. This trend is expected to continue, making renewable energy sources more accessible and affordable for homeowners worldwide. As such, investors should consider the potential returns from adopting solar power technologies.
The market for solar panels for homes has shown consistent growth over the past decade, with a global installed capacity reaching over 800 gigawatts in 2021. This expansion is attributed to various factors, including supportive government policies, advancements in technology, and growing environmental concerns. For investors, the long-term prospects are promising. According to industry reports, solar energy could meet up to 40% of global electricity demands by 2050, making it a key player in the transition towards sustainable energy sources. This shift presents an excellent opportunity for borrowers to invest in solar panels for homes with attractive return on investment (ROI) potential.
Moreover, the financial benefits extend beyond the initial installation costs. Homeowners with solar panels can enjoy substantial savings on their utility bills, with some systems even generating more electricity than they consume. For investors considering loans, understanding borrower requirements is crucial. Typically, banks and lenders offer financing options for up to 100% of the project cost, with interest rates varying based on market conditions and creditworthiness. A well-planned investment strategy can leverage these funds to maximize returns over time. For instance, a study by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) revealed that solar PV systems can provide positive cash flows for up to 25 years, making them reliable long-term investments.
In summary, the future of solar energy for homes is promising, offering investors substantial long-term gains and financial stability. By embracing advancements in technology and understanding borrower requirements, investors can secure lucrative opportunities in the renewable energy sector. As the global shift towards sustainable energy continues, solar panels for homes will remain a compelling investment choice for those seeking both environmental and economic benefits.
