Solar panels for homes offer significant financial and environmental benefits, with global installations growing by over 60% in 2021. Key advantages include reduced energy bills and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Adoption requires considering roof structure, local regulations, financing options, and incentives like federal tax credits and state rebates, which can reduce upfront costs by 20-40%. Choosing the right system involves understanding energy needs, roof characteristics, and panel types. Installation includes assessment, site preparation, mounting, wiring, adherence to standards, and financial considerations. Maintenance, focusing on regular cleaning and inspections, is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency.
In the quest for sustainable living and energy independence, solar panels for homes have emerged as a powerful solution. As global awareness of climate change grows, homeowners are increasingly seeking renewable energy sources to power their residences. This practical guide delves into the intricacies of adopting solar panels, addressing common concerns and misconceptions. We provide an in-depth breakdown, from understanding the technology to navigating financial considerations and installation processes. By the end, readers will be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions about harnessing the sun’s energy for their homes, naturally contributing to a greener future.
Understanding Solar Panels for Homes: Basics Explained
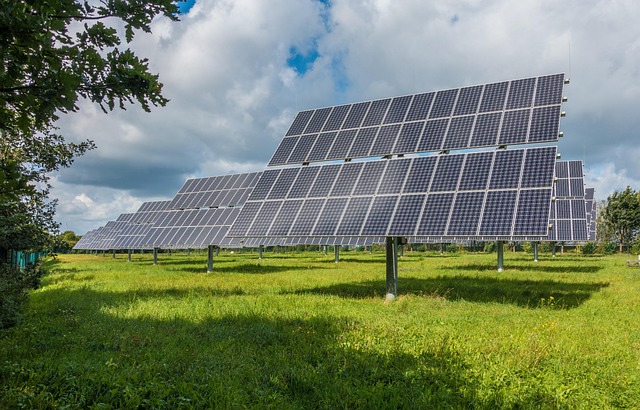

Solar panels for homes have emerged as a powerful tool for homeowners looking to reduce energy costs and their carbon footprint. Understanding how these technologies work is essential for any buyer considering solar panel installation. At its core, solar power harnesses the energy from sunlight using photovoltaic (PV) cells, which convert sunlight directly into electricity. This clean and renewable energy can then be used to power homes, businesses, and even electric vehicles.
One of the key benefits of solar panels for homes is their ability to generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, making them a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. According to recent studies, residential solar installations have seen significant growth worldwide, with over 60% of new solar projects in 2021 being for homes. This trend reflects both the increasing awareness of environmental issues and the declining cost of solar technology, which has made it more accessible to a broader range of borrowers. For instance, the average cost of a solar panel system in the U.S. has dropped by nearly 70% over the past decade, making it an increasingly attractive investment for homeowners looking to save on their energy bills.
However, transitioning to solar power isn’t as straightforward as simply installing panels. Borrowers must also consider various factors, such as roof structure and shade analysis, local regulations and permitting requirements, and available incentives and financing options. For example, understanding the orientation and angle of your roof is crucial for optimal sunlight exposure, while navigating the borrowing process involves assessing interest rates, loan terms, and potential tax benefits. Data from the U.S. Department of Energy indicates that homeowners who take advantage of federal tax credits and state rebates can reduce their initial investment by 20-40%. Therefore, a thorough understanding of solar panels for homes, combined with careful financial planning, is essential to make informed decisions and maximize the benefits of this renewable energy technology.
Benefits and ROI of Installing Solar Panels at Home
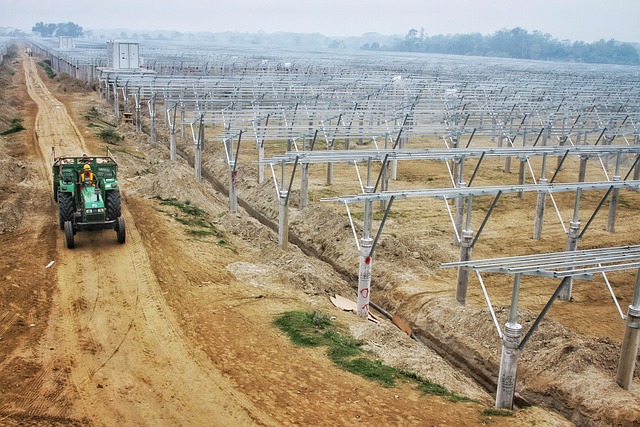

The benefits of installing solar panels for homes go beyond environmental considerations, offering significant financial advantages for homeowners. One of the most compelling aspects is the potential for substantial savings on energy costs. Solar panels harness the power of the sun, providing a clean and renewable source of electricity. This shift from traditional energy providers can lead to long-term savings, especially in regions with high electricity rates. For instance, a study by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) shows that the average household spending on solar panel installation has decreased by 70% over the past decade, making it an increasingly attractive option for borrowers looking to reduce their energy bills.
Additionally, many governments and local authorities offer incentives and grants to encourage the adoption of solar panels for homes. These rewards can include tax credits, rebates, or net metering policies. Borrowers interested in solar panel installation should explore these financial benefits, as they can significantly impact the overall return on investment (ROI). For example, homeowners in certain U.S. states can receive a 26% federal tax credit for installing qualifying solar systems, further reducing the upfront costs and increasing the potential savings over time. When considering solar panels for homes, understanding these financial incentives and their eligibility criteria is essential for maximizing the ROI.
The environmental impact of solar energy is well-documented, but the economic benefits are equally impressive. With proper planning and strategic financing options, the installation of solar panels can be a sound investment. Borrowers should evaluate their long-term energy needs, local climate conditions, and available incentives to determine the optimal time to invest in solar panel technology. By doing so, they can ensure not only a greener future but also a financially prudent decision that could pay off for years to come.
Choosing the Right Solar Panel System for Your Home

Choosing the right solar panel system for your home is a crucial step in transitioning to clean energy. As a borrower considering solar panels for homes, understanding your unique needs and available options is essential. The first consideration is identifying your energy consumption patterns. Examining your utility bills over the past year can provide valuable insights into your average monthly electricity usage. This data will guide you in selecting a solar panel system that aligns with your household’s demands. For instance, larger households or those with high energy-consuming appliances may require more substantial systems to achieve significant savings.
Another critical factor is assessing your roof’s physical characteristics. Solar panels for homes are installed on rooftops, so the structural integrity and orientation of your roof play a pivotal role. Ideally, your roof should face south (in the Northern Hemisphere) or north (in the Southern Hemisphere) to capture maximum sunlight. Additionally, consider the space available; larger solar panel systems can generate more electricity but may demand ample rooftop real estate. Regularly maintained roofs with minimal obstructions, such as trees or nearby buildings, are also preferable for optimal panel performance.
Borrowers should also explore different types of solar panels for homes, such as monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film options. Each technology has unique efficiencies and cost implications. Monocrystalline panels, for example, offer higher efficiency rates but come with a premium price tag. Polycrystalline panels are more affordable but slightly less efficient. Thin-film solar panels, though the least expensive, have lower power outputs and may require more space to achieve comparable energy production. When making your decision, consider local climate conditions and available incentives or rebates to optimize both performance and cost savings from your solar panel system investment.
Installation Process: Step-by-Step Guide to Solar Panels

The installation process of solar panels for homes involves several key steps designed to ensure optimal energy production and system efficiency. It begins with a thorough assessment of your home’s roof or designated space to determine the best layout and panel configuration. This includes evaluating shade patterns, structural integrity, and available area—all crucial factors in maximizing the benefits of solar panels for homes. Once this evaluation is complete, professionals proceed with preparing the site by cleaning and inspecting the surface to guarantee a secure installation.
Next, the actual mounting of the solar panels takes place. The most common types of mounts are roof-mounted (either on top of existing shingles or using a rack system) or ground-mounted (typically in open spaces). These mounts provide stability and protection from environmental factors while keeping panels at an ideal angle for sunlight absorption. After the mounts are securely fastened, the solar panels themselves are attached, followed by the wiring and connector installation. This step involves running cables to a central inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) energy produced by panels into alternating current (AC) usable in your home or feed into the grid.
Throughout this process, borrowers considering solar panels for homes should ensure their chosen provider adheres to industry standards and regulations. It’s also vital to verify that local building codes allow for solar installations and understand any associated permits required. Financial aspects, such as loan options and potential tax incentives, play a significant role in making solar panels for homes more accessible. Borrowers can leverage government programs and private financing to offset installation costs and enjoy long-term energy savings. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and checks every few years, ensures the system operates at peak efficiency over its lifetime.
Maintaining and Maximizing Performance of Solar Panels for Homes
Maintaining and maximizing the performance of solar panels for homes is crucial for any homeowner looking to make the most of their investment. Regular cleaning and inspection are essential components of this process. Dust, dirt, and debris can accumulate on solar panels over time, reducing their efficiency by up to 25%. A simple cleaning routine using a soft brush or garden hose can prevent this buildup. Additionally, shading from trees or neighboring structures can significantly impact performance; periodic trimming or rearranging landscaping may be necessary to ensure optimal sunlight exposure.
Monitoring the health of solar panels is another vital aspect. Regularly check for signs of damage such as cracked or loose panels, corroded components, or unusual temperature fluctuations. Many modern solar systems come with monitoring features that send alerts when performance drops below expected levels. Utilization of these tools can help identify issues early on, enabling prompt repair or replacement before efficiency declines significantly. For instance, a study by the U.S. Department of Energy found that regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of solar panels by 20-30 years.
When it comes to solar panels for homes, borrowers should be aware of specific requirements aimed at maximizing performance and longevity. Lenders often mandate professional inspections as part of the loan process, ensuring panels meet safety standards and are properly installed. Moreover, some financing programs may offer incentives for homeowners who agree to routine maintenance contracts or use certified installers, further enhancing the overall efficiency of their solar systems. For borrowers considering solar panels for homes, understanding these requirements upfront can streamline the loan application and ensure a smoother transition to clean energy.
